Quality control of special pharmaceutical organics
Identification with UV spectroscopy
 UV-1800
UV-1800
The European Pharmacopoeia guideline for instruments details adjustment parameters and promotes a common understanding of their performance. Up to nine checks are done to calibrate and validate an instrument.
The most important requirement of scanning UV instruments is their capability to perform 1 nm resolution. For the standard requirements of the Pharmacopoeia an instrument such as the Shimadzu UV-1800 is a good solution. This double beam spectrophotometer is equipped with a slit of 1 nm. The proof of performance is the signal resolution of a mixture prepared from Hexane and Toluene. The instrument applies all Shimadzu and Pharmacopoeia validation criteria. It automatically integrates validation in one level and automated tests with certified standards in another level.
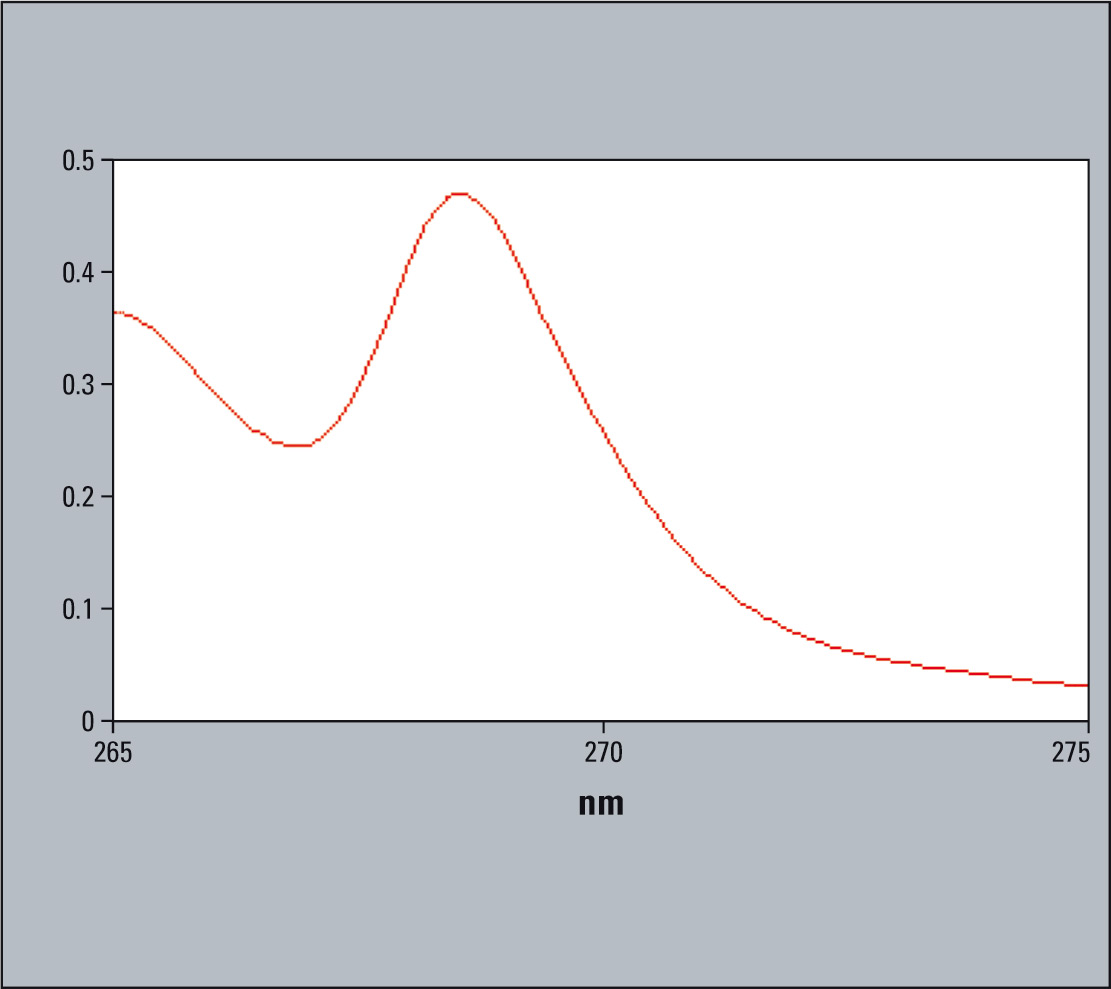 Figure 1: Graph-hexane/toluene resolution
Figure 1: Graph-hexane/toluene resolution
The UV-1800 is a recommended system because of its stability in baseline and the accuracy of each data point over the complete measurement range.
This system can be used for simple quality control of pharmaceutical substances according to the requirements of EP, USP and FDA.
Some applications needing much higher resolution are also of interest. In these cases a high-performing instrument is required, in particular when the analysis shall be performed with a resolution of lower than 1nm.
An example of such a high-resolution request is the measurement of Gadodiamide in UV range in combination with a Shimadzu UV-2550 spectrophotometer.
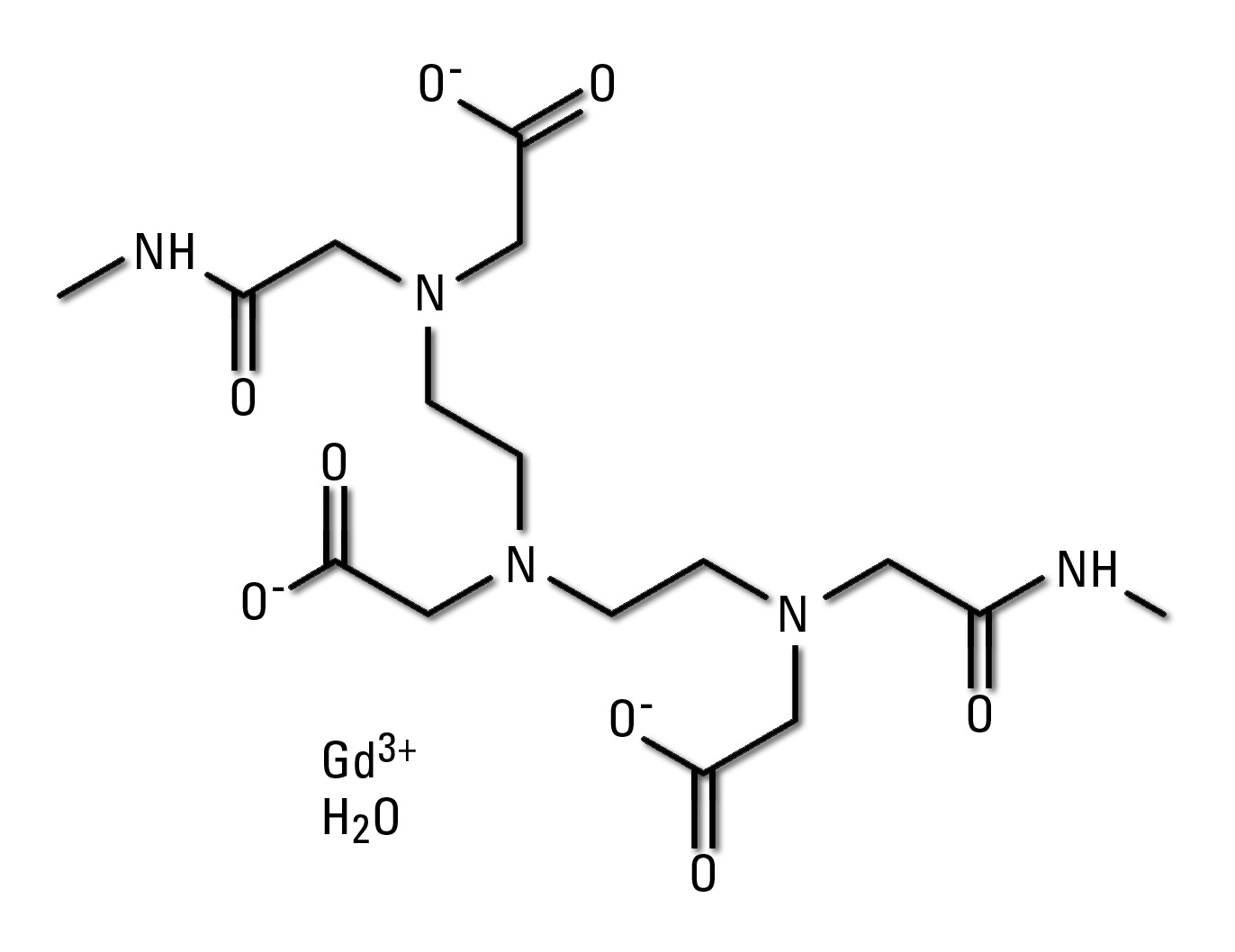 Figure 4: Chemical structure of the Gadodiamide Molecule
Figure 4: Chemical structure of the Gadodiamide Molecule
The analysis
Gadodiamide (known under the brand name of Omniscan, for example) is used as a magnetic resonance (MR) contrast medium. Gadodiamide is used as an indicator for the neuro part or whole body of a scan. From a chemical point of view, this substance is a chelate complex which is a molecular structure of negatively charged groups surrounding a metallic ion. In this case, it is the Gd (Gadolinium) ion. The substance is also explained in the following formula as Gd-DTPA-BMA. The characteristic is a linear chelate, uncharged and with low osmolarity.
For the identification high resolution is needed for the signal shape of position 247.3 and 253.1 nm.
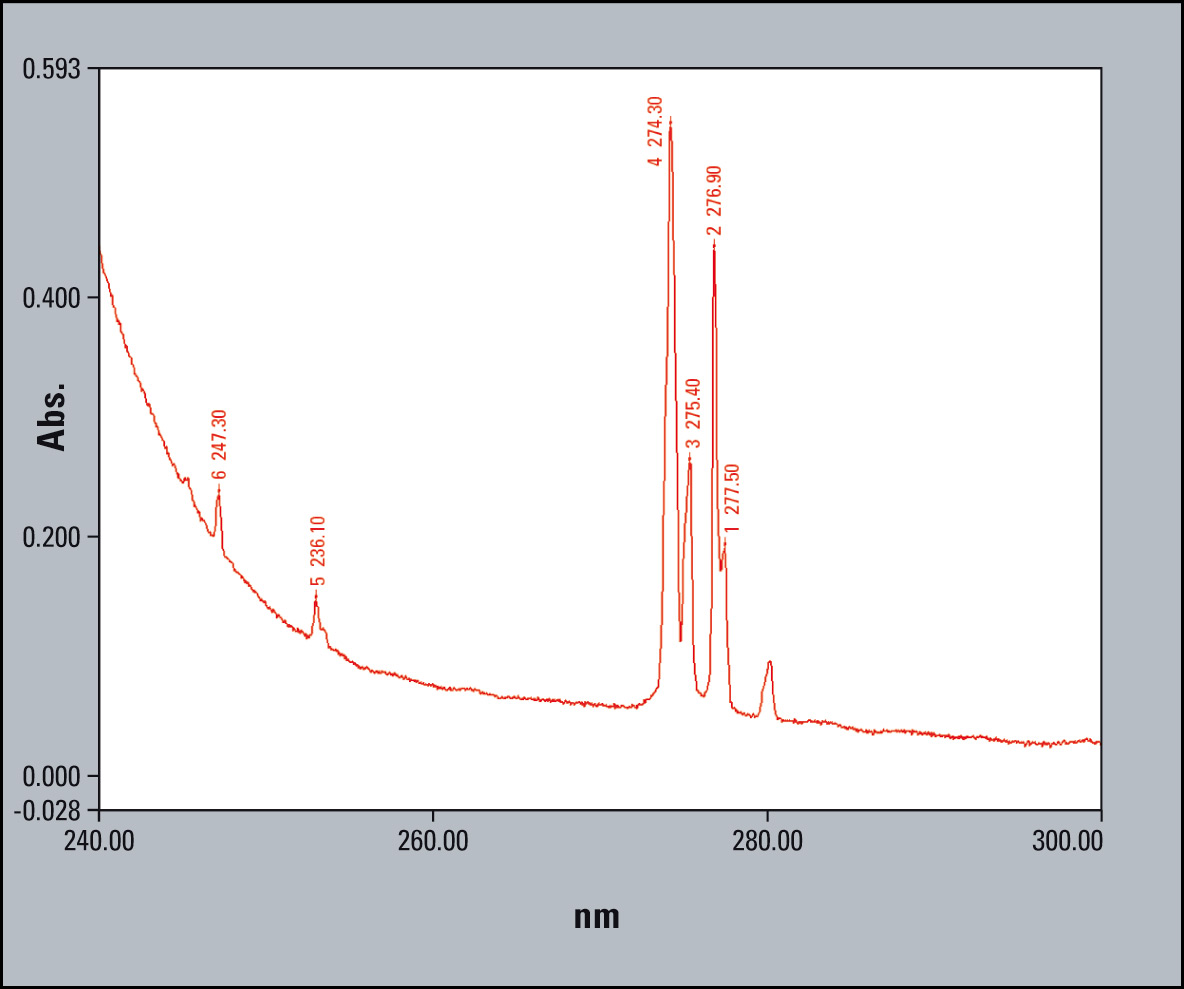
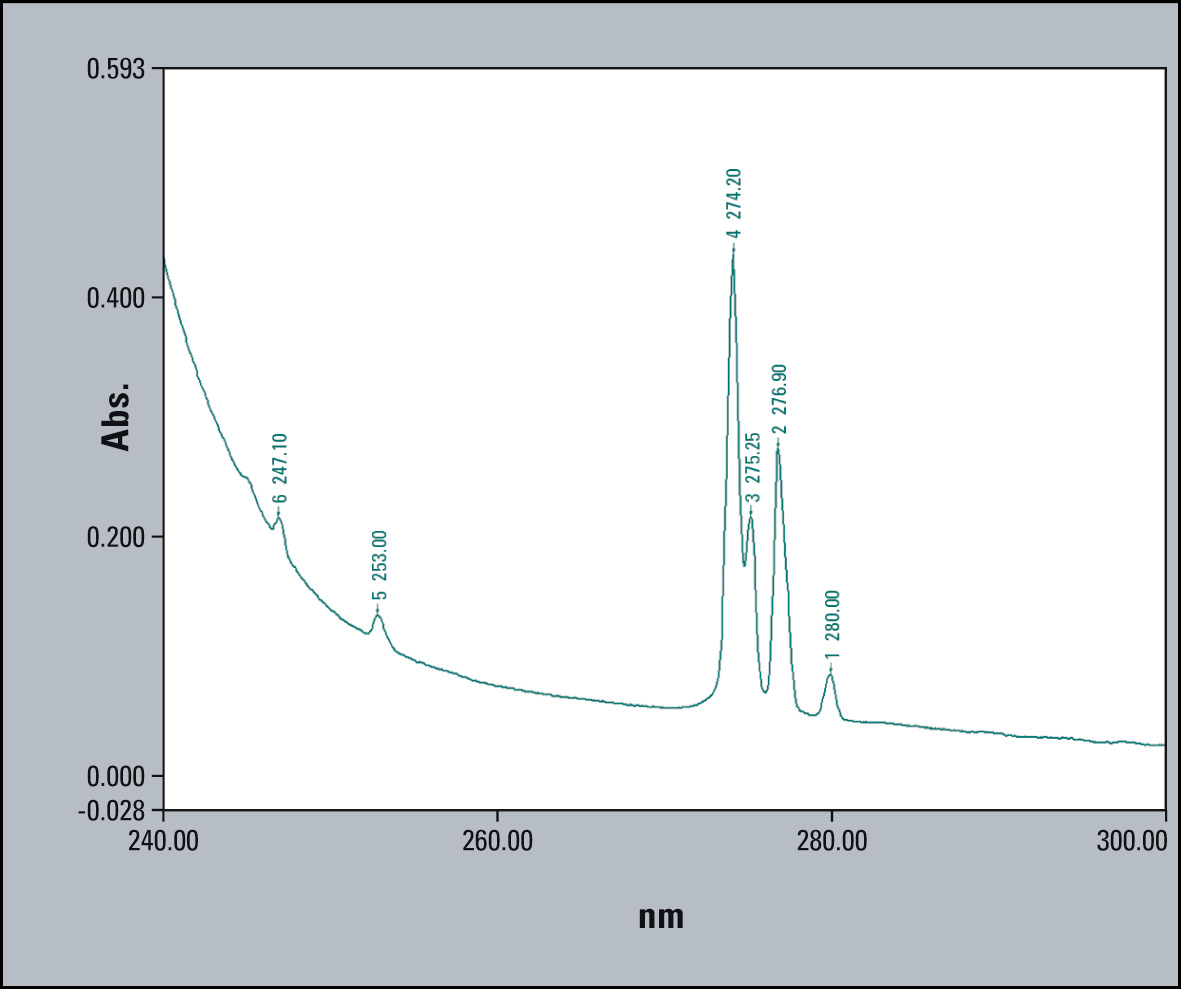 Figure 2 and 2a: Spectra of Gadodiamide in the UV-range with automated peak detection; the spectra were measured with different resolution; the red spectrum was with 0.2 nm resolution and the green spectrum with 0.5 nm
Figure 2 and 2a: Spectra of Gadodiamide in the UV-range with automated peak detection; the spectra were measured with different resolution; the red spectrum was with 0.2 nm resolution and the green spectrum with 0.5 nm
In figure 2 the spectrum with 0.2 nm is shown on the left side, and the same substance with 0.5nm resolution is shown on the right side. Automatic determination of peak position can verify both signals of interest only with higher resolution out of the high basic absorption at the area from 260 to 240 nm. The signal at 247 nm disappears into a shoulder when the measurement is done with 1 nm resolution. An automated detection is impossible and manual detection becomes difficult. It will result in time consuming activities of spectrum manipulation.
The UV-2550 instrument was applied. The spectra generated were measured in the absorbance mode.
Following parameters were investigated under high resolution measurement with the UV-2550:
Measurement Properties
Wavelength Range: 240 to 300 nm
Scan Speed: Very Slow
Sampling Interval: 0.1 nm
Scan Mode: Single
Path Length: 10 mm; 1 cm standard quartz cell
Instrument Properties
Instrument Type: UV-2550
Measuring Mode: Absorbance
Slit Width: 0.2 nm
Light Source Change Wavelength: 360 nm
S/R Exchange: Normal
 Table 1: First characteristics of Gadodiamide*
Table 1: First characteristics of Gadodiamide*
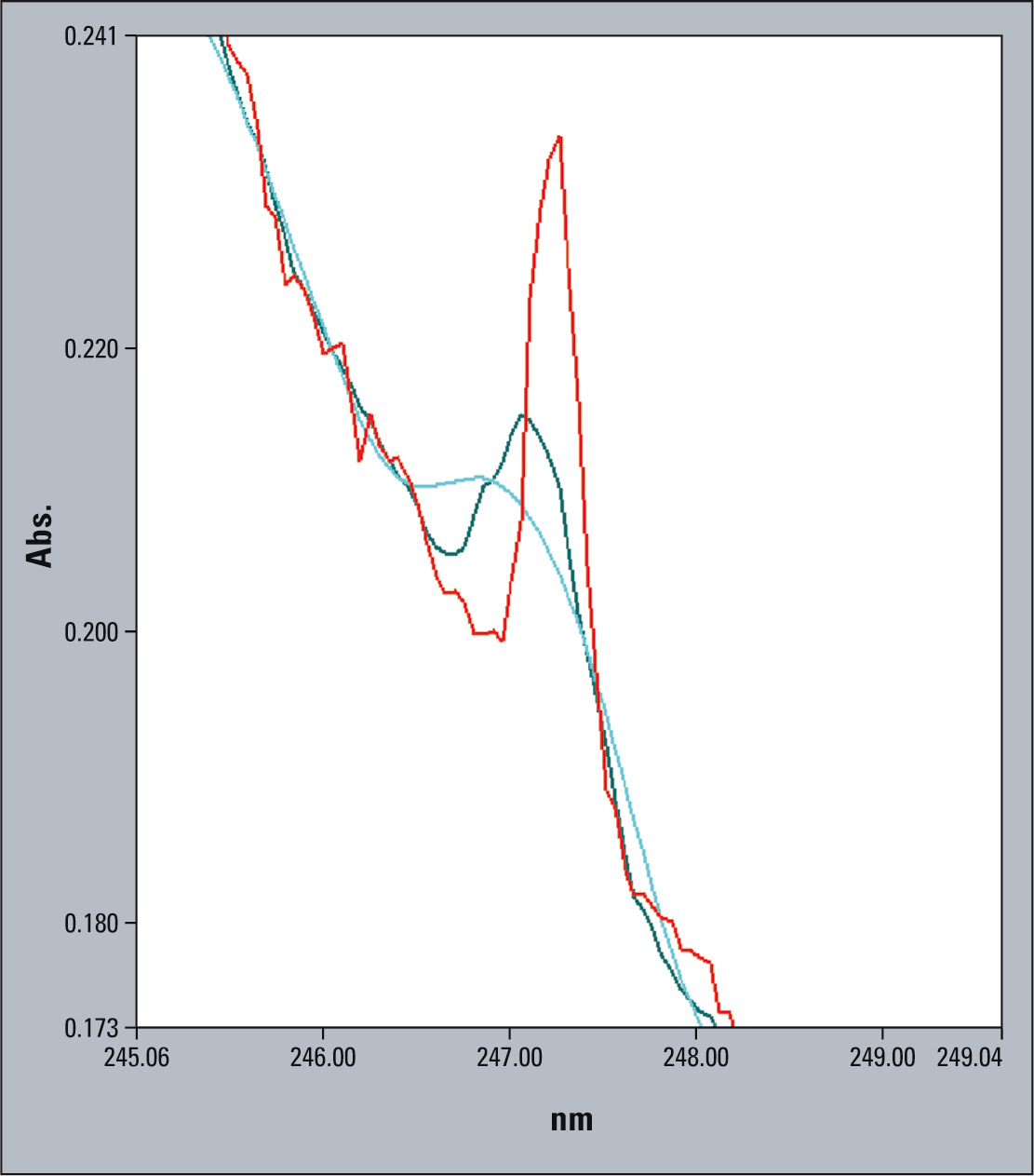 Figure 3: Zoom into the region of interest. The dark green line has 0.5 nm resolution and the red one 0.2 nm slit selection. The signal developed by the 0.2 nm slit is much higher and sharper. Identification of the signal is much more accurate. The light green spectrum has 1 nm resolution, showing the difficulty of detection.
Figure 3: Zoom into the region of interest. The dark green line has 0.5 nm resolution and the red one 0.2 nm slit selection. The signal developed by the 0.2 nm slit is much higher and sharper. Identification of the signal is much more accurate. The light green spectrum has 1 nm resolution, showing the difficulty of detection.
*Sources:
- http://chembank.med.harvard.edu
- Wikipedia