»Plug und Play« disease screening solution?
The MALDI-8020 in screening for Sickle Cell Disease
In 2006, the World Health Assembly passed a resolution recognizing the Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) as a public health priority and called on countries to tackle the illness. This resolution was also adopted by the United Nations in 2009. In this context, numerous screening programs have been set up in many laboratories around the world.
SCD is a group of inherited red blood cell disorders. It is caused by abnormal hemoglobin (HbS) resulting from mutations in the hemoglobin beta. The condition was first described as early as 1910. Today, approximately 80 % of sickle cell disease cases are found in tropical regions, particularly sub-Saharan Africa, but have also increased in Europe in recent decades due to migration.
How to meet the needs of public health measures
Disease screening programs are front-line public health measures, and as such must be based on robust analytical methods and data-processing software. Cost effectiveness is a further requirement and has prompted the implementation of high-throughput screening units that reduce item costs. Lastly, the greatest possible use of automation enables the medical team to focus exclusively on abnormal samples. The Shimadzu MALDI-MS (Mass Spectrometer) together with technology packages from Biomaneo company in Dijon, France including sample processing kit, data processing and management software were designed to address these challenges.
Two-tier procedure for more accurate results
Screening programs are typically organized in two-tier procedures: The first tier is normally a routine method which must be able to detect the pathological samples with a single mutation and classify unambiguously into three groups: heterozygotes without HbS variants, heterozygotes with HbS variants and HbS homozygotes. The second level is based on a second standard reference method and is used to confirm the first results.
Screening for hemoglobinopathies can be performed with newborns, in order to ensure early care for children. This care at an early age enables a considerable increase in life expectancy. The second option of screening can be carried out in young adults or adults in the case of primary prevention, enabling people to know their status of homozygous AA or heterozygous XS. People who inherit one sickle cell gene and one normal gene have sickle cell trait (SCT) and are heterozygote XS. People with SCT do not usually have any SCD symptoms but can pass the trait on to their children.
Efficient analytical method
Neonatal screening is usually performed centrally in specialized laboratories. The biological sample used for this screening is a dry blood spot on blotting paper.
The use of MALDI-MS in hospital laboratories has already proved its value, in particular through the identification of micro-organisms (use of VITEK®MS for example). MALDI-MS techniques meet the requirements of screening. Specifically, the techniques used must meet the criteria of automation, sensitivity, resolution, robustness, speed of analysis, resistance to high analytical rates and ease of use.
Through the implementation of screening for sickle cell disease, Biomaneo company has shown that the MALDI-8020 benchtop mass-spectrometer meets the quality criteria mentioned above and makes the use of MALDI-MS in laboratories easier, convenient and fast.
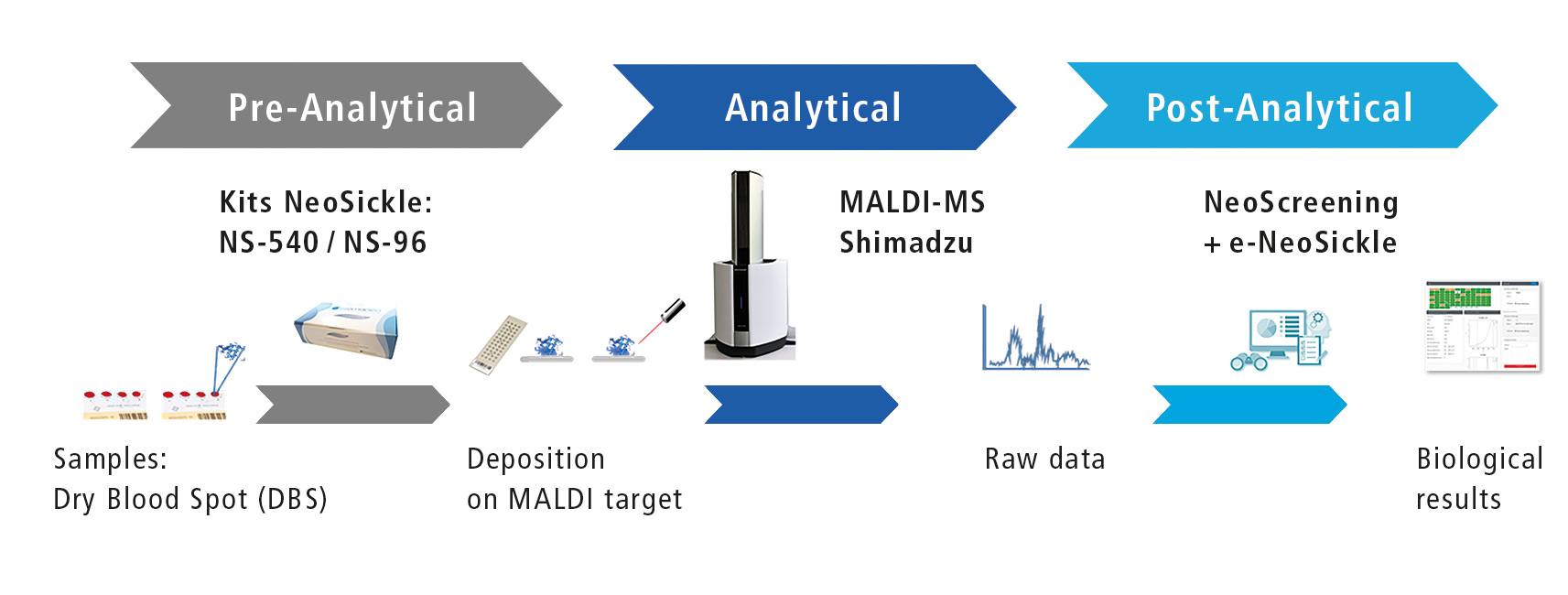 Figure 1: Workflow of automated screening
Figure 1: Workflow of automated screening
New method, high-throughput, easy to use
Biomaneo has developed a ‘plug and play’ analytical solution that combines a sample treatment kit, the MALDI-MS technology and a software to interpret results automatically by combining them with clinical data (figure 1).
The first NeoSickle® kit was developed in two versions: the first is dedicated to high-throughput analysis using a robot; for this a support to use the Fleximass target of MALDI-8020 was specifically created (figure 2), and the robot script adapted.
The second version is a kit for labs which analyses nearly 200 samples per day manually. The Fleximass target is adapted for both of these options.
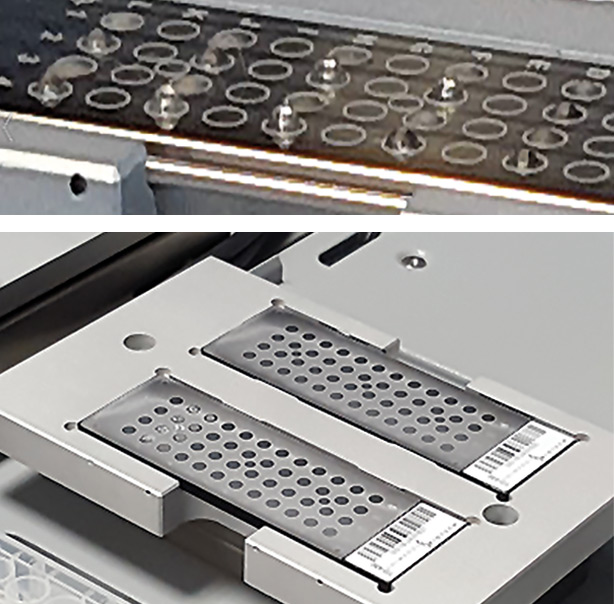 Figure 2: Specific support for Fleximass target
Figure 2: Specific support for Fleximass target
Resolution is an extremely important criterion in the analyses of hemoglobinopathies
Due to abnormal hemoglobin, SCD arises from mutations in the hemoglobin beta gene (HbS) in which the glutamic acid is substituted by valine at position 6, resulting in 30 Da lowering of the mass. The first NeoSickle solution is based on the whole protein analysis which needs a sufficient resolution at the mass of approximately 15 kDa. Figure 3 shows the resolution capability of the MALDI-8020 in line with expectations to detect the different hemoglobin chains HbS, HbA and HbF.
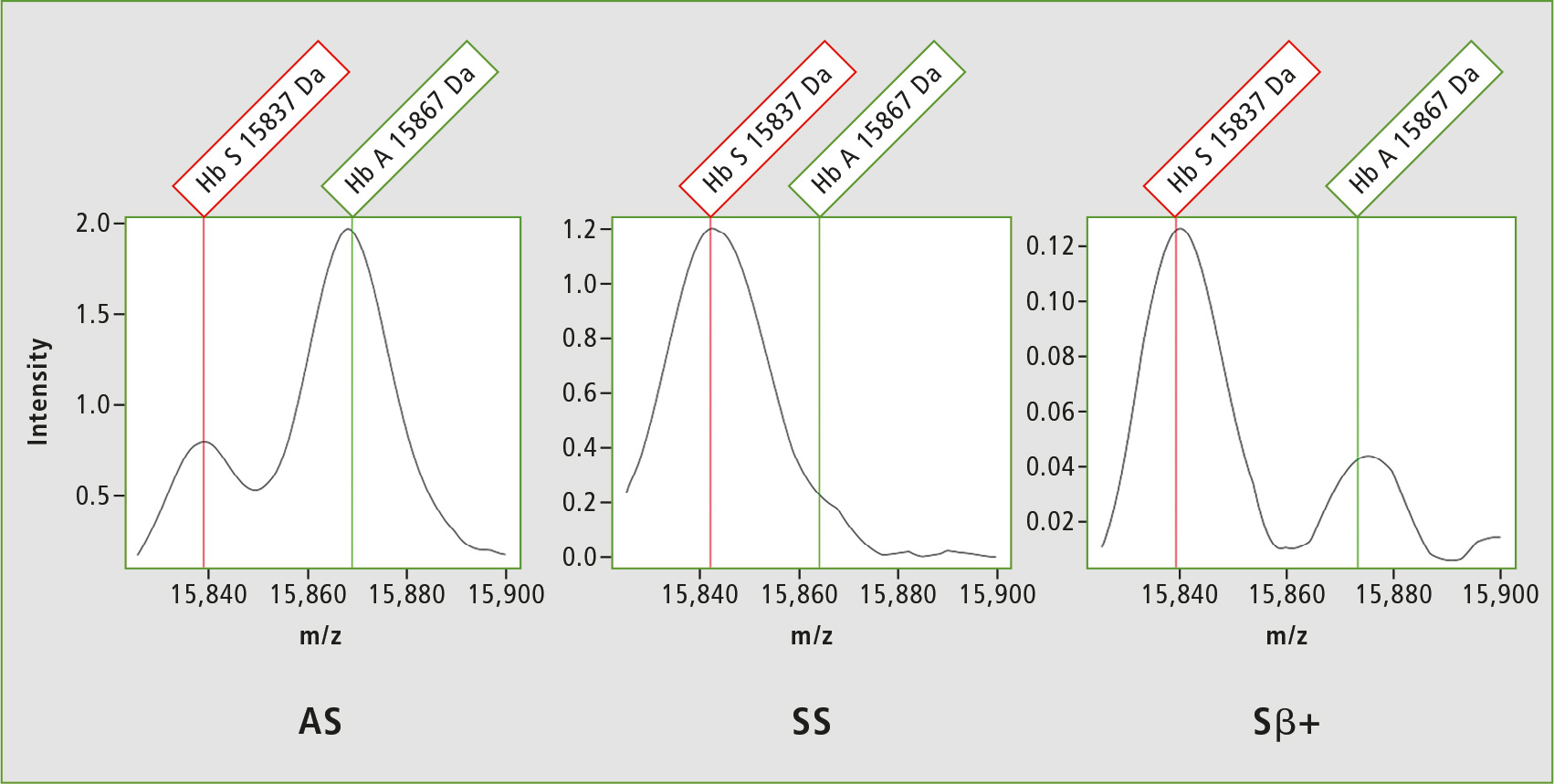 Figure 3: Spectrum obtained from Heterozygote AS, Sbeta+ and Homozygote SS samples with the detection of hemoglobin HbA and HbS chains
Figure 3: Spectrum obtained from Heterozygote AS, Sbeta+ and Homozygote SS samples with the detection of hemoglobin HbA and HbS chains
With this first approach, it is not possible to separate the other chains of hemoglobin variants such as HbC and HbE which have a mass difference of 1 Da compared to the normal HbA chain. For this reason, the second approach used by Biomaneo consists of analyzing hemoglobin chains peptides, and the resolution and dynamic range of the MALDI-8020 benchtop allows for separation of the peptides of interest. Figure 4 illustrates the possibility to separate the sample groups homozygote AA or heterozygotes AE.
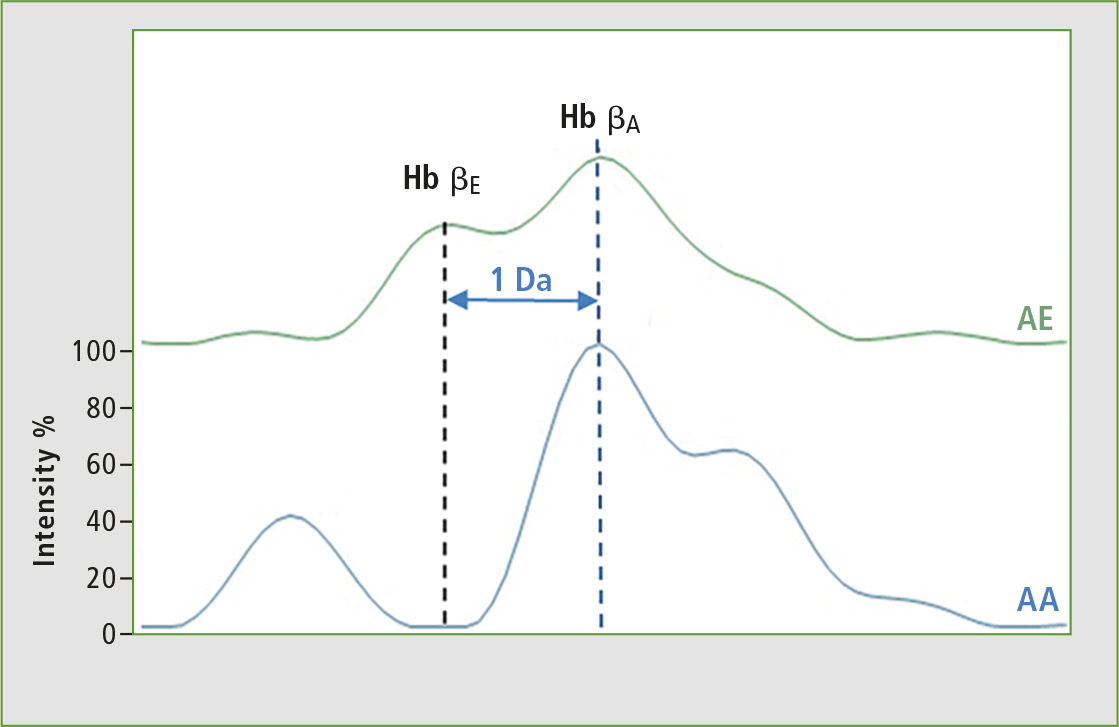 Figure 4: Analysis of specific peptides from hemoglobin chains HbE and HbA
Figure 4: Analysis of specific peptides from hemoglobin chains HbE and HbA
Sensitivity and dynamic range of detection
The other crucial criteria in SCD screening are the sensitivity and dynamic range of detection. In fact, the sample from very premature newborns has a very low percentage, less than 3 % of the adult hemoglobin chain compared to other compounds in the sample (foetal beta hemoglobin and alpha hemoglobin chain). Detection and differentiation of the HbS beta hemoglobin chain in these samples is very important in order to avoid re-blood sampling and/or misclassify the newborns. The study demonstrates the high quality of the MALDI-8020 instrument with a percentage of classification of very premature babies above 90 %.
Screening for SCD is performed in centralized laboratories analyzing a large number of samples per day. The technology used for screening must therefore be automated and/or convenient to use for the technician. Usability is an indispensable criterion for the establishment and use of mass spectrometry in analytical laboratories. The usability of the MALDI-8020 benchtop is clearly an advantage for the laboratory where the number and turnover of technicians, not specialists of MALDI-MS, is very high.
MALDI-8020 is the system of choice
The MALDI-8020 meets these criteria with well-calibrated and standardized methods. Use of the MALDI-8020 is intuitive, allowing its rapid integration into laboratory studies and facilitating the work of technicians. In addition, the system is very compact and can be easily placed on any laboratory bench.
Throughput in screening laboratories is a strong requirement to be considered in the introduction of new analytical methods. The spectra acquisition method implemented in the NeoSickle solution combined with the performance of the MALDI-8020 benchtop allows the analysis of a MALDI target containing 48 samples in less than three minutes. This throughput, including the change of target in the instrumentation, will allow 576 analyses per hour.
For SCD, the main French screening laboratory analyses about 600 samples per day, meaning over 150,000 samples per year or about 20 % of births. Less than six hours of analysis per day with the MALDI-8020 would be sufficient to screen all newborns in a single laboratory.
Fully serves the needs of screening laboratories
Beyond the daily throughput, the last criterion concerns the robustness of the instrumentation over time and the low maintenance requirements. To maintain instrument performance with an objective of 500,000 tests per year, Shimadzu’s MALDI-8020 provides TrueClean automated source cleaning. It can be used to clean the extraction electrode in-situ without breaking instrument vacuum; it is an automated and rapid (< 10 min) UV laser-based procedure. Moreover, the wide-bore ion optics minimize the risk of source contamination over time, providing a robust platform.
These characteristics and results demonstrate the suitability of the MALDI-8020 bench-top mass spectrometer for the detection of hemoglobinopathies and more generally for the high-throughput analysis of complex blood samples. It very clearly satisfies the needs of screening laboratories.
The power and speed of MALDI instruments means that they will very rarely be used full time for just a single application. For hospitals or laboratories, it is effective to optimize the investments made in these technologies. System versatility is an important financial criterion to be taken into account. For laboratories with a small number of screening analyses, the advantage of the MALDI-8020 is the management of acquisition parameters. Indeed, the acquisition methods integrate all the parameters necessary to control the instrumentation, making the MALDI-8020 applicable for multiple applications without the risk of interfering with individual analyses.
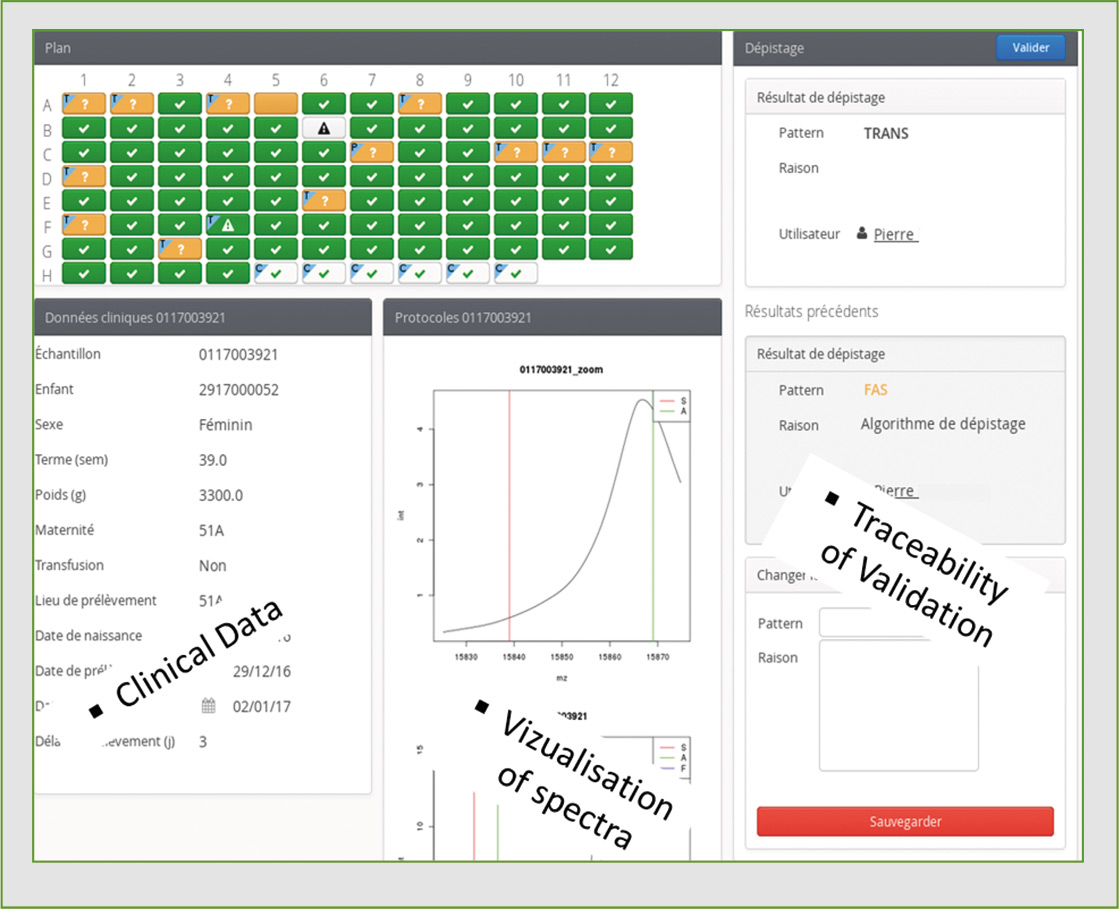 Figure 5: Screenshot of the NeoScreening LIMS after analysis of one plate
Figure 5: Screenshot of the NeoScreening LIMS after analysis of one plate
To enhance the power of automated high-throughput data production by the MALDI-8020, Biomaneo has developed a software package (LIMS: Laboratory Information Management System) to integrate the results and assist in the interpretation of mass spectrometry data. The LIMS NeoScreening® allows production of the files necessary to control the MALDI-8020 and launch an analysis run, while also retrieving data automatically and then processing and classifying each sample result.
Conclusion
The speed of acquisition and the simplicity of changing methods makes the MALDI-8020 benchtop ideal for many applications and an indispensable measuring instrument for biochemistry laboratories.
In the context of SCD screening, the MALDI-8020 meets all requirements. This compact, simple to use and high-performance instrument allows screening in most cases.
NeoSickle® is a registered trademark of Biomaneo.
NeoScreening® is a registered trademark of Biomaneo.